In the world of modern technology, agents in artificial intelligence (AI) play a central role in the development of smart systems. These agents are the driving force behind automation, learning, and decision-making in machines. Whether it’s a chatbot, autonomous vehicle, or recommendation system, the presence of intelligent agents makes AI applications possible and powerful.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what agents in artificial intelligence are, how they work, the different types, and their applications across industries. By the end, you’ll understand not just the theory behind these agents but also their real-world impact and importance.
What Are Agents in Artificial Intelligence?
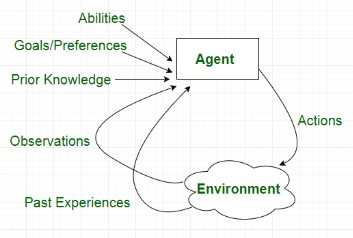
At its core, an agent in artificial intelligence is an entity that perceives its environment through sensors and acts upon that environment using actuators. The goal of the agent is to perform actions that maximize some notion of success or achieve specific goals.
A simple example of an AI agent is a thermostat. It senses room temperature and turns the heating or cooling system on or off to maintain a desired temperature. In more complex systems, agents in artificial intelligence might process vast amounts of data, learn from past experiences, and make predictions or decisions accordingly.
Structure of AI Agents
To understand agents in artificial intelligence, it’s helpful to break down their architecture. Generally, an AI agent consists of the following components:
-
Sensors – These are used to perceive the environment. In robots, this could include cameras, microphones, and proximity sensors.
-
Actuators – These perform actions. For robots, actuators could be motors or mechanical arms.
-
Perception – The process of interpreting sensor data to form a view of the environment.
-
Decision-Making – The logic or algorithms the agent uses to decide what to do next.
-
Learning – Some agents can improve over time using machine learning techniques.
Understanding this architecture helps explain how agents in artificial intelligence can operate autonomously and adaptively in dynamic environments.
Types of Agents in Artificial Intelligence
AI agents can be classified into several types based on their complexity and capabilities:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
These respond directly to sensor input with predefined rules. They do not consider the history of perceptions. For example, a robot that turns left every time it detects an obstacle is a simple reflex agent.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
These use internal models of the world to handle partial observability and complex environments. They maintain a state of the world to inform decisions.
3. Goal-Based Agents
These agents can evaluate future actions based on a goal. They choose actions that help achieve their objective rather than just reacting to current input.
4. Utility-Based Agents
These agents not only aim to achieve goals but also evaluate how desirable those goals are. This allows them to choose among conflicting goals based on a utility function.
5. Learning Agents
Among the most sophisticated, learning agents improve their performance by learning from interactions with the environment. They include components for learning, performance, and critique.
Understanding the variety of agents in artificial intelligence allows developers and researchers to choose the right kind of agent for a specific problem.
Applications of AI Agents
The presence of agents in artificial intelligence is widespread across numerous domains. Here are a few examples:
1. Healthcare
AI agents assist in diagnosing diseases, monitoring patient vitals, and suggesting treatments. Virtual nursing assistants are a growing example of AI agent use.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on AI agents to interpret sensor data, make navigation decisions, and respond to traffic in real time.
3. Finance
In financial markets, trading bots are intelligent agents that analyze market trends and execute trades without human intervention.
4. Customer Service
Chatbots are among the most familiar agents in artificial intelligence, handling thousands of customer interactions simultaneously and improving response times.
5. Smart Homes
From lighting to climate control, smart home devices often operate as AI agents, learning user preferences and optimizing operations accordingly.
These applications underscore how agents in artificial intelligence are transforming everyday life and enhancing efficiency across sectors.
Challenges in Building AI Agents
While the concept of agents in artificial intelligence is well-defined, building effective agents is not without its challenges:
-
Environment Complexity: Real-world environments are unpredictable and noisy.
-
Data Limitations: Some agents struggle due to lack of quality data for training.
-
Ethical Considerations: Decisions made by AI agents can have significant societal impacts.
-
Security Risks: Malfunctioning or hacked AI agents can pose safety and privacy threats.
Despite these hurdles, ongoing research continues to improve the robustness and reliability of AI agents.
Future of Agents in Artificial Intelligence
As AI technology evolves, so too will the capabilities of its agents. Future agents in artificial intelligence will likely become more autonomous, emotionally intelligent, and capable of working alongside humans in collaborative environments.
Trends such as explainable AI (XAI) will ensure that the decisions made by these agents are understandable and transparent. Additionally, the integration of AI agents with other emerging technologies like quantum computing and blockchain could open up entirely new possibilities.
Conclusion
Agents in artificial intelligence are at the heart of how machines interact intelligently with the world. Whether they are simple rule-based systems or advanced learning entities, these agents are revolutionizing how tasks are automated, decisions are made, and services are delivered.
By understanding the different types, functions, and applications of AI agents, we can better appreciate their role in shaping our future. As industries continue to embrace AI, the significance of intelligent agents will only grow, making it essential for professionals, developers, and curious learners to grasp the fundamentals of this transformative technology.