Accurate and timely assessment of pupil response is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring various neurological conditions. Among the many tools available for pupil assessment, the Neurological Pupil Index (NPi) has emerged as a significant advancement. This article will compare the NPI with other traditional and contemporary pupil assessment tools, exploring their methodologies, applications, and relative advantages.
The Role of Pupil Assessment in Neurology
Pupil assessment is a vital component of a comprehensive neuro exam, providing insights into the functionality of the autonomic nervous system and the integrity of the brainstem. The size, shape, and reactivity of the pupils can indicate underlying neurological conditions such as traumatic brain injury, stroke, and increased intracranial pressure. Over the years, various tools and techniques have been developed to evaluate pupil response, each with its own strengths and limitations.
The Neurological Pupil Index (NPi)
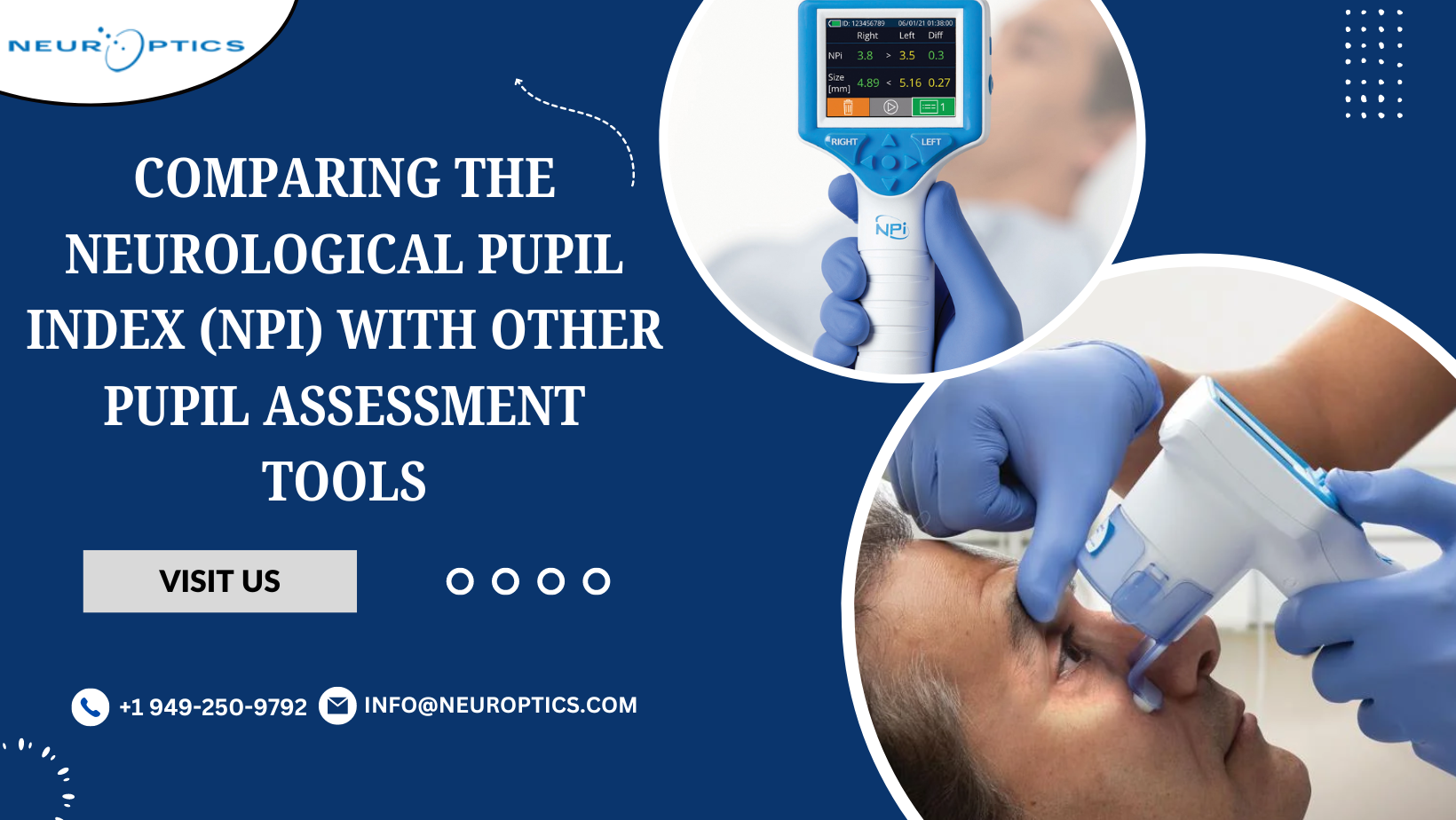
The Neurological Pupil Index (NPi) is a quantitative measure that provides a standardized assessment of pupil reactivity. Developed through advanced pupillometry technology, the NPI evaluates the percent change in pupil size in response to light stimuli. This tool offers a numerical value that reflects the overall neurological function, with a lower NPI indicating potential abnormalities.
Methodology of NPI
The NPI utilizes an automated pupillometer to measure various parameters, including initial pupil size, constriction velocity, and dilation velocity. By analyzing these factors, the NPI algorithm generates a single index value that ranges from 0 to 5, with values closer to 5 indicating normal pupil function.
Advantages of NPI
Standardization: The NPi provides a consistent and objective measurement, reducing inter-observer variability.
Sensitivity: The NPi can detect subtle changes in pupil reactivity that may not be noticeable through manual assessment.
Ease of Use: Automated pupillometers are user-friendly, requiring minimal training for healthcare professionals.
Comprehensive Data: The NPi encompasses multiple aspects of pupil dynamics, offering a holistic view of neurological function.
Traditional Pupil Assessment Tools
Penlight Examination
One of the oldest and most commonly used methods for pupil assessment is the penlight examination. During this procedure, a healthcare professional shines a light into the patient’s eye and observes the pupil’s response.
Methodology of Penlight Examination
The penlight examination involves direct visual observation of the percent change in pupil size and reactivity to light. The examiner assesses the speed and extent of pupil constriction and dilation, noting any asymmetry or irregularities.
Advantages of Penlight Examination
Accessibility: Penlights are inexpensive and widely available in clinical settings.
Simplicity: This method is straightforward and requires no specialized equipment.
Immediate Results: Results are available instantaneously, allowing for rapid assessment.
Limitations of Penlight Examination
Subjectivity: The accuracy of the penlight examination depends heavily on the examiner’s experience and skill.
Limited Sensitivity: Subtle changes in pupil reactivity may go undetected.
Variability: Inter-observer variability can lead to inconsistent results.
Ruler Measurement
Another traditional method involves using a ruler to measure the pupil diameter. This technique can provide a basic quantitative assessment but lacks the sophistication of more advanced tools.
Methodology of Ruler Measurement
The ruler measurement technique involves placing a ruler near the patient’s eye and measuring the diameter of the pupil under various lighting conditions.
Advantages of Ruler Measurement
Cost-Effective: Rulers are inexpensive and do not require any technological investment.
Simple: The method is easy to perform and understand.
Limitations of Ruler Measurement
Accuracy: Measuring pupil diameter with a ruler can be imprecise and prone to human error.
Subjectivity: Like the penlight examination, this method relies on the examiner’s judgment.
Limited Data: This method only provides information on pupil size, not reactivity dynamics.
Contemporary Pupil Assessment Tools
Automated Pupillometry
Automated pupillometry represents a significant advancement in pupil assessment, offering precise and objective measurements.
Methodology of Automated Pupillometry
Automated pupillometers use infrared technology to capture high-resolution images of the pupil. The device measures various parameters, such as initial size, constriction velocity, and latency, and provides detailed data on pupil reactivity.
Advantages of Automated Pupillometry
Precision: Automated pupillometers deliver highly accurate measurements.
Objectivity: The technology reduces human error and subjectivity.
Comprehensive Analysis: These devices can analyze multiple aspects of pupil dynamics.
Limitations of Automated Pupillometry
Cost: Automated pupillometers can be expensive, limiting their availability in some settings.
Training: Proper use of these devices requires training and familiarity with the technology.
Portable Digital Pupillometers
Portable digital pupillometers offer a balance between traditional methods and advanced automated technologies, providing a practical solution for many clinical settings.
Methodology of Portable Digital Pupillometers
These devices use digital sensors to measure pupil size and reactivity. They often include software that analyzes the data and provides a comprehensive report.
Advantages of Portable Digital Pupillometers
Portability: These devices are lightweight and easy to transport, making them ideal for various clinical environments.
Efficiency: Portable digital pupillometers provide quick and accurate measurements.
Data Storage: Many of these devices can store and track patient data over time.
Limitations of Portable Digital Pupillometers
Cost: While less expensive than fully automated systems, these devices can still be costly.
Calibration: Regular calibration is necessary to maintain accuracy.
Comparative Analysis
Accuracy and Sensitivity
The NPi, with its advanced algorithm and comprehensive data analysis, offers superior accuracy and sensitivity compared to traditional methods like penlight neuro exam and ruler measurement. Automated pupillometry and portable digital pupillometers also provide high accuracy, but the NPi’s standardized index adds an extra layer of precision.
Objectivity and Standardization
The NPI excels in providing an objective and standardized assessment, reducing inter-observer variability that is common with manual methods. Automated and portable digital pupillometers also offer objectivity, but the NPI’s single numerical value simplifies interpretation and comparison.
Ease of Use and Accessibility
Traditional methods like penlight examination and ruler measurement are simple and accessible but lack the sophistication and accuracy of modern tools. Automated pupillometry and portable digital pupillometers require more training and investment but offer significant improvements in data quality. The NPi, while requiring the use of automated pupillometers, strikes a balance by providing detailed, standardized assessments that are relatively easy to interpret.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The advent of the Neurological Pupil Index (NPi) has significant clinical implications, particularly in critical care and emergency settings where rapid and accurate neurological assessment is paramount. For instance, in cases of traumatic brain injury or stroke, timely detection of changes in pupil reactivity can guide immediate interventions and improve patient outcomes. The NPI’s ability to provide a quick, reliable, and reproducible measure of neurological status allows healthcare providers to make more informed decisions.
Integration with Other Neurological Tools
The NPi can be integrated with other neurological assessment tools to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of a patient’s condition. Combining NPI data with other diagnostic modalities, such as neuroimaging and electroencephalography (EEG), can enhance the overall understanding of a patient’s neurological function. This multimodal approach can lead to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans, ultimately improving patient care.
Advancements in Technology
As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of pupillometry and the NPi are likely to expand. Future developments may include more portable and cost-effective devices, increased integration with electronic health records (EHRs), and enhanced algorithms that provide even more detailed analyses of pupil dynamics. These innovations will make the NPi and similar tools more accessible and valuable in a wider range of clinical settings.
Conclusion
The Neurological Pupil Index (NPi) represents a substantial advancement in pupil assessment. By offering a standardized, objective, and compassionate measure of pupil reactivity, the NPI addresses many of the limitations associated with traditional methods. While automated and portable digital pupillometers also provide significant benefits, the NPI’s unique ability to deliver a comprehensive and easy-to-interpret index value makes it a valuable addition to the toolkit of healthcare professionals conducting neuro exams. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of advanced tools like the NPi will undoubtedly enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of neurological assessments.