1. Introduction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) and Peyronie’s disease are two conditions that can significantly affect a man’s sexual health and overall well-being. Understanding the relationship between these conditions is crucial, as it can help prevent and manage them effectively. This article aims to explore whether ED can lead to Peyronie’s disease by examining the definitions, causes, symptoms, and connections between these two conditions.
2. Understanding Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is defined as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. This condition can be caused by various factors, both physical and psychological. Common causes of ED include:
- Cardiovascular diseases (e.g., hypertension, atherosclerosis)
- Diabetes
- Hormonal imbalances (e.g., low testosterone)
- Neurological disorders (e.g., multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease)
- Psychological issues (e.g., stress, anxiety, depression)
- Lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of exercise)
Symptoms of ED typically include:
- Difficulty achieving an erection
- Trouble maintaining an erection during sexual activity
- Reduced sexual desire
ED is a prevalent condition, affecting approximately 30 million men in the United States. Its likelihood increases with age, but it can also affect younger men, particularly those with underlying health issues or unhealthy lifestyle habits.
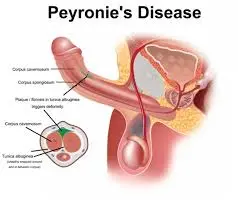
3. Understanding Peyronie’s Disease
Peyronie’s disease is characterized by the development of fibrous scar tissue, known as plaques, inside the penis. This condition leads to curved, painful erections and can significantly impact sexual health and function. Symptoms of Peyronie’s disease include:
- A noticeable bend or curve in the penis during an erection
- Pain during erections or sexual intercourse
- Presence of hard lumps or plaques under the skin of the penis
- Shortening of the penis
Peyronie’s disease can cause significant distress and interfere with sexual satisfaction and performance. It is estimated that about 1% to 23% of men experience this condition, though the exact prevalence is uncertain due to underreporting.
4. The Connection Between Erectile Dysfunction and Peyronie’s Disease
There is a potential link between erectile dysfunction and Peyronie’s disease. Men with ED are at a higher risk of developing Peyronie’s disease, and the presence of one condition can exacerbate the other. Here’s how ED can contribute to the development of Peyronie’s disease:
Mechanisms and Medical Theories: One theory suggests that repeated unsuccessful attempts at achieving or maintaining erections can cause microtrauma to the penile tissue. These micro traumas may lead to the formation of scar tissue, which is a hallmark of Peyronie’s disease. Additionally, men with ED often experience fewer frequent erections, which may reduce the natural stretching of penile tissue and contribute to fibrous plaque formation.
5. Risk Factors and Common Causes
Several risk factors are shared between ED and Peyronie’s disease, making it important to address these factors to prevent both conditions.
Shared Risk Factors:
- Age: Both conditions are more common in older men.
- Trauma: Penile injuries or repeated microtrauma can lead to both ED and Peyronie’s disease.
- Genetics: A family history of either condition can increase the risk.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and other chronic illnesses are common risk factors.
Untreated ED and Peyronie’s Disease: Leaving ED untreated can increase the risk of developing Peyronie’s disease. Men with untreated ED may experience more frequent penile injuries due to manual manipulation or rough handling during attempts to achieve an erection.
6. Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of both ED and Peyronie’s disease is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Symptoms to Watch For:
- ED Symptoms: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, reduced sexual desire.
- Peyronie’s Disease Symptoms: Curvature of the penis, pain during erections, hard lumps or plaques, shortened penis.
Diagnostic Methods:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will examine the penis for signs of curvature, plaques, or other abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: This imaging test can identify scar tissue and assess blood flow in the penis.
- X-rays or MRI: In some cases, these imaging tests may be used to get a detailed view of the penile structures.
Importance of Early Diagnosis: Early diagnosis of Peyronie’s disease can prevent the condition from worsening and improve treatment outcomes. Men experiencing symptoms of ED or Peyronie’s disease should seek medical advice promptly.
7. Treatment Options
Treatment options for erectile dysfunction and Peyronie’s disease vary, and addressing one condition can often alleviate the other.
Treatments for Erectile Dysfunction:
- Medications: Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (e.g., Malegra 200, Super P Force) are commonly prescribed to improve blood flow to the penis.
- Lifestyle Changes: Improving diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol consumption can enhance erectile function.
- Therapy: Counseling or sex therapy can address psychological factors contributing to ED.
Treatments for Peyronie’s Disease:
- Medications: Fildena 100 can help reduce plaque formation and penile curvature.
- Surgery: Surgical options may be considered for severe cases that do not respond to other treatments. Procedures include plaque incision or removals and penile implants.
- Therapy: Physical therapy, including penile traction devices, can help stretch and straighten the penis.
Treating ED to Prevent Peyronie’s Disease: Effectively managing ED can reduce the risk of developing Peyronie’s disease. Improving erectile function can decrease the likelihood of penile injuries and the formation of scar tissue.
8. Prevention Strategies
Preventing both ED and Peyronie’s disease involves maintaining good overall health and taking specific steps to protect penile health.
Tips for Maintaining Penile Health:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports cardiovascular health and erectile function.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves blood flow, reduces stress, and helps maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoiding Tobacco and Limiting Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can damage blood vessels and contribute to ED and Peyronie’s disease.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, therapy, and maintaining a work-life balance can improve sexual health.
Importance of Regular Medical Check-Ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify and manage risk factors for ED and Peyronie’s disease. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
9. When to Seek Medical Advice
It is important to seek medical advice if you experience symptoms of ED or Peyronie’s disease.
Signs That Indicate a Need for Professional Evaluation:
- Persistent difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection
- Noticeable curvature or pain in the penis
- Presence of hard lumps or plaques under the skin of the penis
- Shortening of the penis
Benefits of Consulting a Healthcare Provider Early: Early consultation with a healthcare provider can lead to prompt diagnosis and effective treatment, preventing the conditions from worsening.
What to Expect During a Medical Consultation: During a consultation, a healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history, conduct a physical examination, and order diagnostic tests to identify the underlying cause of symptoms. Based on the findings, they will recommend appropriate treatment options.
10. Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between erectile dysfunction and Peyronie’s disease is essential for preventing and managing these conditions. Both ED and Peyronie’s disease can significantly impact a man’s sexual health and quality of life. By addressing risk factors, seeking early medical advice, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, men can reduce their risk of developing these conditions and improve their overall well-being. If you experience symptoms of ED or Peyronie’s disease, do not hesitate to seek professional help. Taking proactive steps can lead to better health outcomes and a more satisfying sexual life.